Read Our Latest Blogs
Learn the latest on a variety of health topics
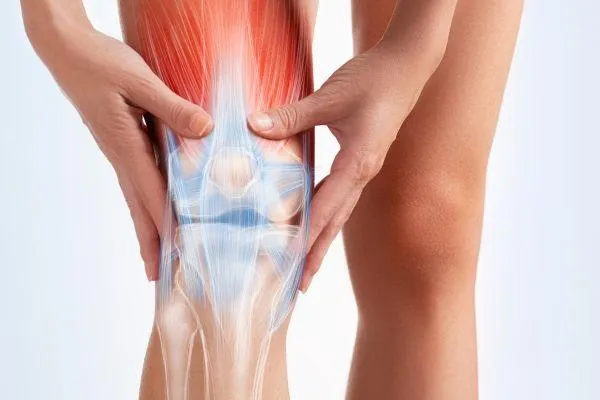
Knee Arthritis and Treatment Options: From Conservative to Less Conservative Approaches
“I don't deserve this award, but I have arthritis and I don't deserve that either.” - Jack Benny
Introduction:
The knee is a crucial joint in the human body, responsible for supporting our weight, facilitating mobility, and allowing us to perform everyday activities with ease. However, like all body parts, it's susceptible to wear and tear. One of the most common ailments affecting the knee is arthritis. This article will shed light on knee arthritis and walk you through various treatment options, evaluating the pros and cons of each – from conservative methods to less conservative ones, including the increasingly popular shockwave therapy.
Knee arthritis typically refers to a condition where the cartilage in the knee joint deteriorates over time, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. The most prevalent forms of knee arthritis are:
1. Osteoarthritis (OA):
A degenerative joint disease, OA is the most common type of arthritis. It's characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone, often due to age or overuse.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the synovium – the lining of the membranes surrounding the knee joint.
3. Post-traumatic Arthritis:
Develops after a knee injury and is similar to osteoarthritis, but the cause is traced back to the injury.
Treatment Options
1. Conservative Approaches
Pros:
Non-invasive: These treatments typically avoid surgery, reducing potential risks.
Lower Cost: Conservative treatments are generally more affordable.
Self-Management: Many of these can be managed independently, allowing for flexibility.
Cons:
Slower or Temporary Relief: Might take time to show results or might offer only temporary relief.
Limited Efficacy: Might not be effective for advanced stages of arthritis.
a. Lifestyle Changes:
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in low-impact exercises, and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain can slow arthritis progression and manage symptoms.
b. Physical Therapy:
Guided exercises can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving stability and reducing pain.
c. Medications:
Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs can manage pain and inflammation.
d. Knee Braces or Orthotics:
Can offer support, reduce pain, and improve stability.
2. Less Conservative Treatments
Pros:
Directly Addressing: Targets the root cause and can offer long-lasting or permanent relief.
Effective for Advanced Cases: Can be beneficial when conservative methods fail.
Cons:
Potential Surgical Risks: Invasive methods come with inherent risks such as infections or anesthesia complications.
Costlier: Generally more expensive than conservative treatments.
a. Corticosteroid Injections: Injected into the knee joint, they can provide rapid relief from inflammation and pain but are not a long-term solution and known to cause damage to cartilage long term.
b. Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Mimicking a naturally occurring substance in the joint, these injections lubricate and cushion the joint, reducing pain.
c. Shockwave Therapy: This involves sending acoustic waves to the knee, promoting regeneration and reparative processes in the bones and soft tissues.
Pros of Shockwave Therapy:
Non-invasive: No surgery or injections involved.
Promotes Natural Healing: Stimulates blood flow and cell regeneration.
Cons of Shockwave Therapy:
Mixed Results: Some patients might benefit more than others. More severe later stages of arthritis may have less significant results.
May Require Multiple Sessions: Several treatments might be needed for optimum results.
d. Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where damaged cartilage or bone fragments are removed.
e. Osteotomy: The bone is cut and realigned to shift weight from a damaged part of the knee to a healthier area.
f. Total or Partial Knee Replacement: Damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial components.
Informed Decision-Making
Seek Expertise: Always begin by consulting a rheumatologist or orthopedic surgeon. They can provide a comprehensive diagnosis and recommend suitable treatments.
Evaluate Severity: Mild arthritis might be managed with conservative treatments, but severe cases might require surgical interventions.
Consider Personal Preferences and Lifestyle: Every individual's tolerance to pain, activity level, and personal preferences differ. What works for one might not work for another.
In conclusion, knee arthritis, while common, need not be debilitating. With a plethora of treatments available, from conservative methods like physical therapy to surgical interventions and innovative treatments like shockwave therapy, there's hope for every individual. As always, ensure you're well-informed and consult with healthcare professionals to make decisions that best align with your health goals and lifestyle.

© 2023 Doctors Health Hub - All Rights Reserved, This site is for informational services and not to be used for the diagnosis and treatment of disease.
This site is not part of the Facebook website or Facebook Inc. Additionally, this site is NOT endorsed by Facebook in any way. FACEBOOK is a trademark of FACEBOOK, Inc.




